WIN has adopted a corporate sustainable development philosophy that supports environmental protection and green production.
WIN is concerned about climate and environmental protection issues and continues to supervise and improve emissions
reduction measures for energy management, greenhouse gas emissions management, air pollution control, water resource management,
and effluents and waste management. We implement these measures and work hard to reduce the impact of the production
process on the environment. WIN established the Environmental Protection, Occupational Health and Safety Policy,
and promotes reduction activities and resource reuse in its EHS policy, in order to fulfill its commitment to
regulatory compliance and environmental protection.
WIN supports and maintains biodiversity and forest conservation, continues to take care of and maintain
vegetation in park areas, and actively pays attention biodiversity issues and development of the Taskforce
on Nature-related Financial Disclosures (TNFD) framework. WIN has formulated the "Biodiversity and No Deforestation Policy"
to lower the impact of environmental changes and habitat destruction on the ecosystem.
To fulfill our commitment to environmental sustainability, we have adopted management systems and certifications related to the environment, and obtained environmental management system (ISO 14001), greenhouse gas (ISO 14064) and energy management system (ISO 50001) certifications.

1,555,831
kWh
Reduced electricity consumption

3,793
ton CO2e
Reduced carbon emissions
334,332
tons
Recycled water
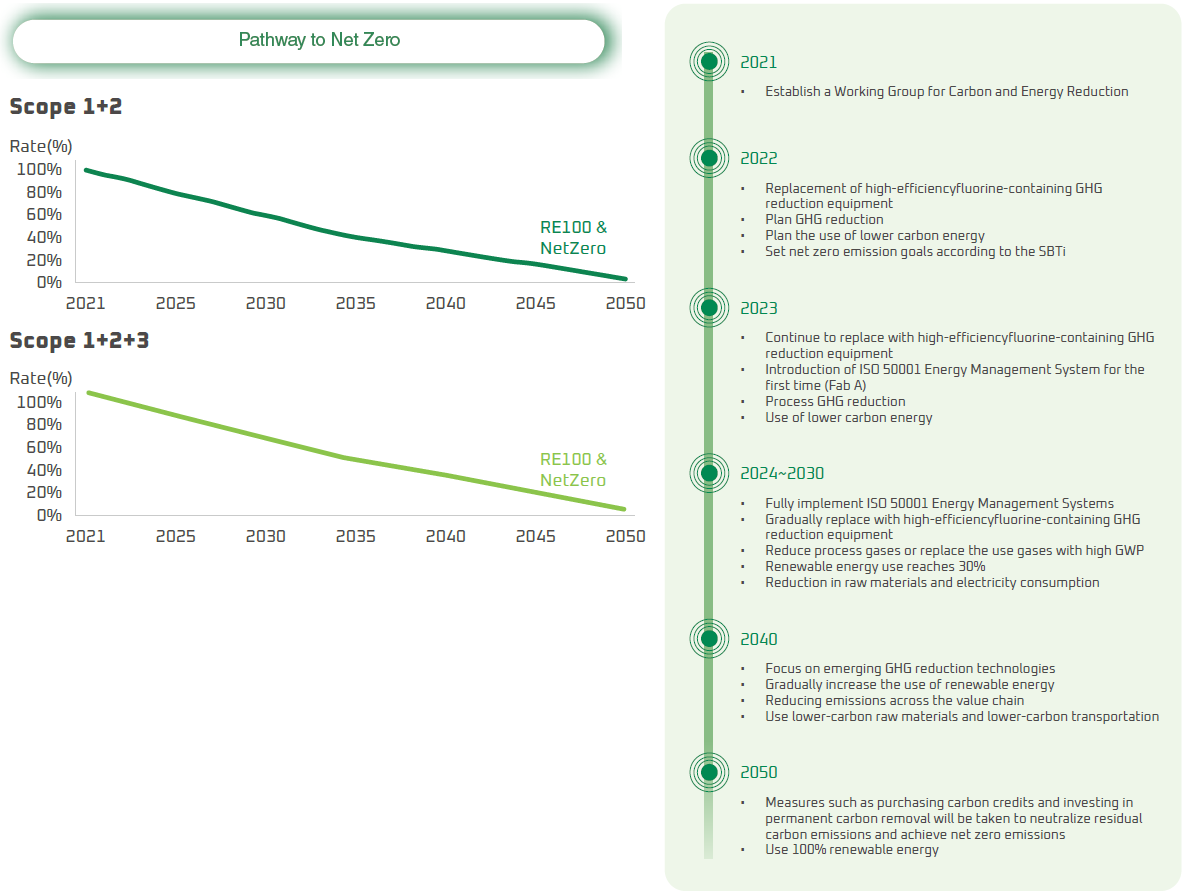
Net Zero Strategy
WIN attaches importance to climate change issues and is dedicating efforts to low carbon transformation. We launched the net zero emissions plan in 2021, and established a Working Group for Carbon and Energy Reduction (changed name to Energy Management Committee from 2023) with the support of Board of Directors and senior executives. In 2022, we referenced and complied with the SBTi Corporate Net-Zero Standard, which uses 2021 as the base year, and set SBTi for Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions that limiting global warming to within 1.5°C (linear reduction over 4.2% a year) with the long-term goal to achieve an absolute reduction of 90% Scope 1+2+3 emissions in 2050 compared with the base year of 2021. We will take related measures to neutralize the remaining carbon emissions and achieve net zero emissions, showing our determination to reduce carbon emissions through our net zero strategy. We will also regularly review whether actual emissions align with the net zero pathway, pay attention to carbon reduction technologies and changes in issues, and continuously adjust the net zero strategy.
Starting from 2023, WIN has actively promoted energy management and gradually introduced the ISO 50001 Energy Management System in each fab. Among them, the Fab A and Fab B have obtained third-party certification. Through systematic management, it continuously improves energy utilization efficiency and achieves the goal of reducing electricity consumption and greenhouse gas reduction.
Climate Change and Greenhouse Gas Management
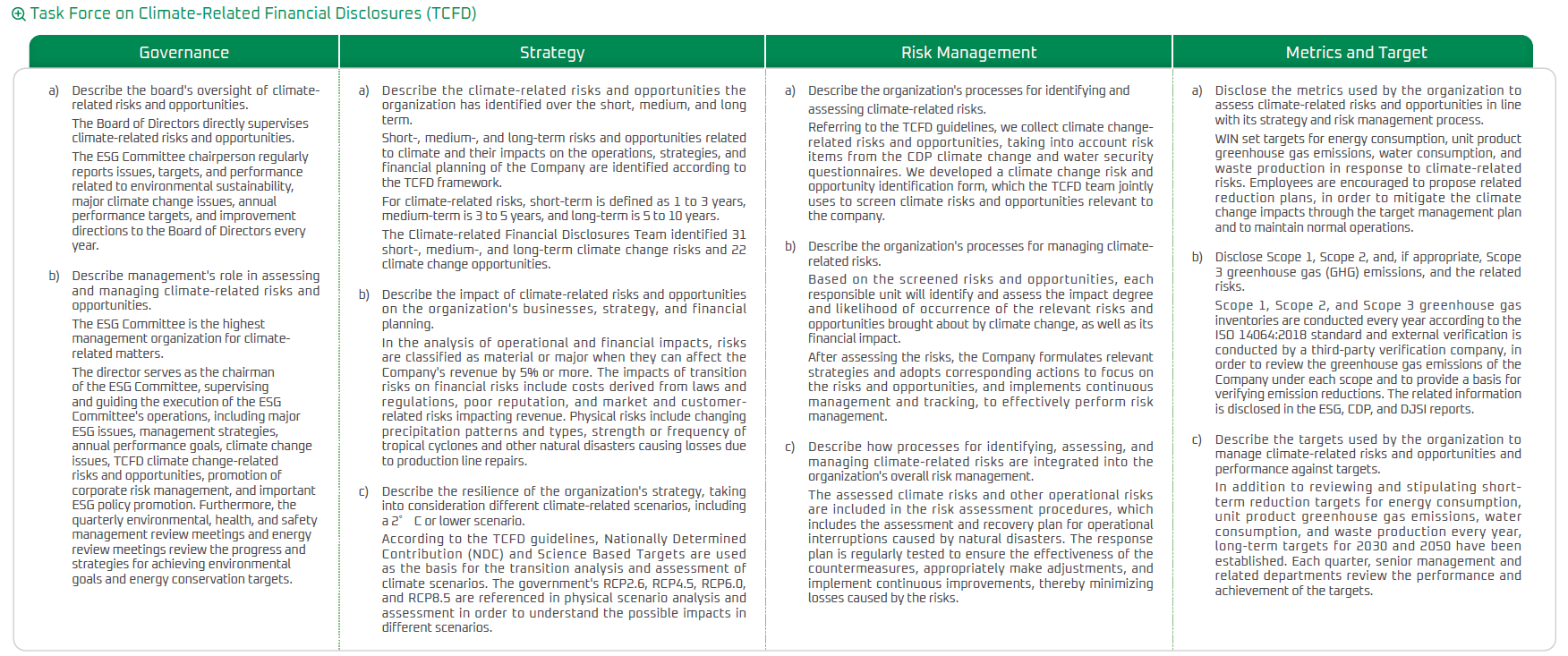
In response to global climate change and low-carbon transition, WIN actively pays attention to the risks and derived opportunities that climate change may bring. With the support of Director on board and senior executives, WIN assembled members of related departments and established the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) team to establish mechanisms and strengthen operations, and formulate strategies and actions in response to climate change based on four aspects: governance, strategy, risk management, and metrics and target. We identified potential risks that may threaten the Company as well as opportunities and the impact of climate-related risks and opportunities on the Company, and regularly review quantitative targets and performance indicators.
Task Force on Climate-Related Financial Disclosures (TCFD)

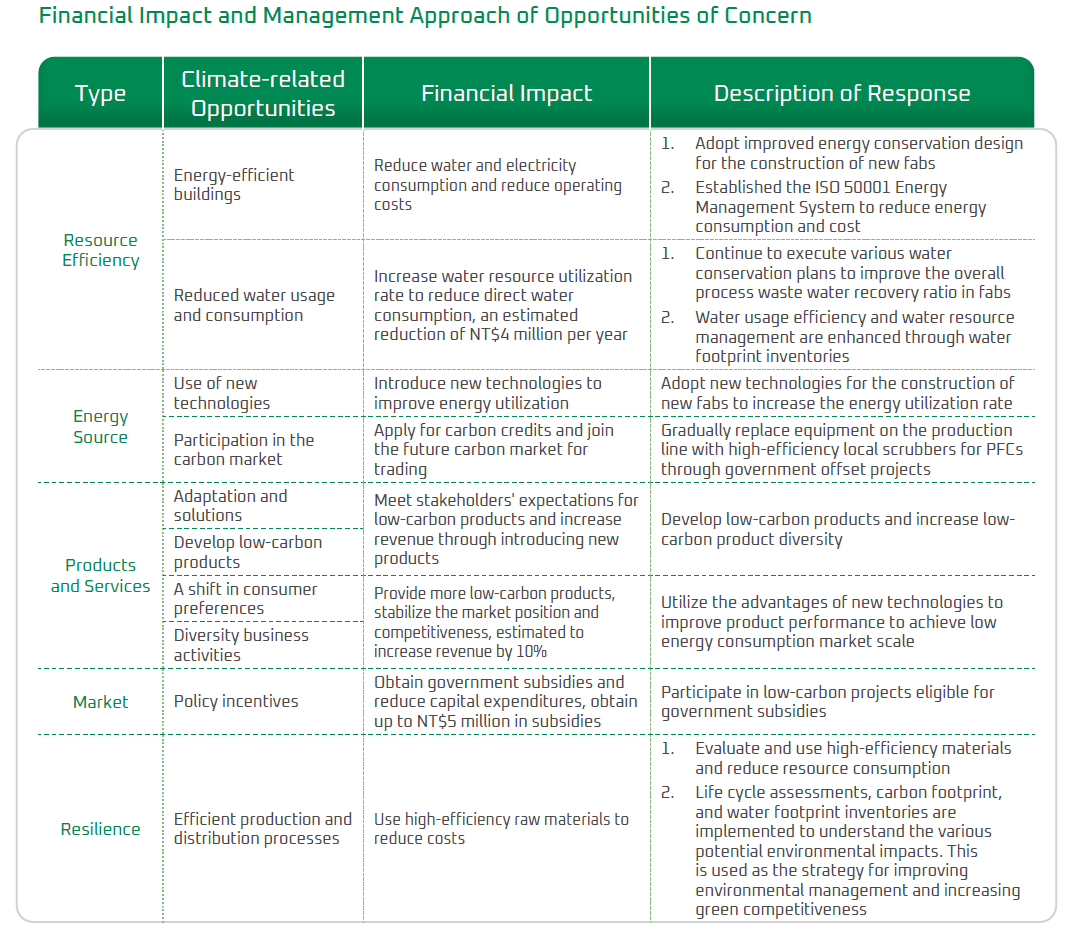
In 2024, the TCFD team identified 23 climate change risks, of which 10 were as risks of concern, including extreme weather, shift in customer preferences, and business reputation, and 18 climate change opportunities, of which 7 were as opportunities of concern, in which key items include improving production efficiency and participation in the carbon market.
WIN set environmental protection policies and targets, and encourages employees to propose carbon reduction, water conservation, and waste reduction plans and develop energy-saving products and services to mitigate global climate emergencies and create a corporate culture of environmental sustainability. Employees that make proposals can win a prize in the EHS proposal contest, employees can also participate the Company's "Innovation / Service / Efficiency Award" with total rewards. Furthermore, the Company actively responds to the Carbon Disclosure Project (CDP) and climate questionnaire of the DJSI, disclosing information on climate issue management and carbon emission data. WIN was selected into the DJSI World Index for the 5 consecutive years in 2024, and was also rated at the "Leadership Level" by the CDP Water Security, and at the "Management Level” by the CDP Climate Change.
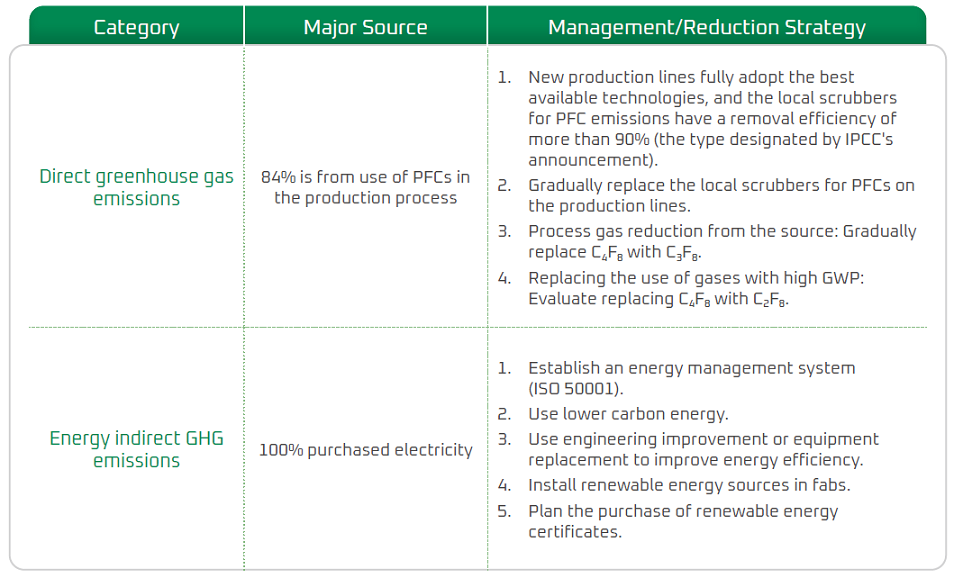
Greenhouse Gas Management
Greenhouse gas emissions are the main cause of climate emergencies. Corporate greenhouse gas management is a main issue of concern to stakeholders. Since 2011, WIN established a standard for GHG inventories in accordance with ISO 14064 and the Guidelines for Greenhouse Gas Inventories by the Climate Change Administration of Ministry of Environment. We regularly inventory the greenhouse gas emissions of our fabs every year and pass third-party verifications. DNV Business Assurance Co., Ltd. conducted the inventory in 2024 to fully understand WIN's greenhouse gas usage and to verify the results of reduction. WIN uses operational control as the inventory boundary, covering the management processes and facilities at all fabs (Fab A, Fab B, and Fab C). The GHG covered by the inventory are: CO2, CH4, N2O、HFCs、PFCs, SF6, NF3. The plants used zero ozone-depleting substances (ODS).
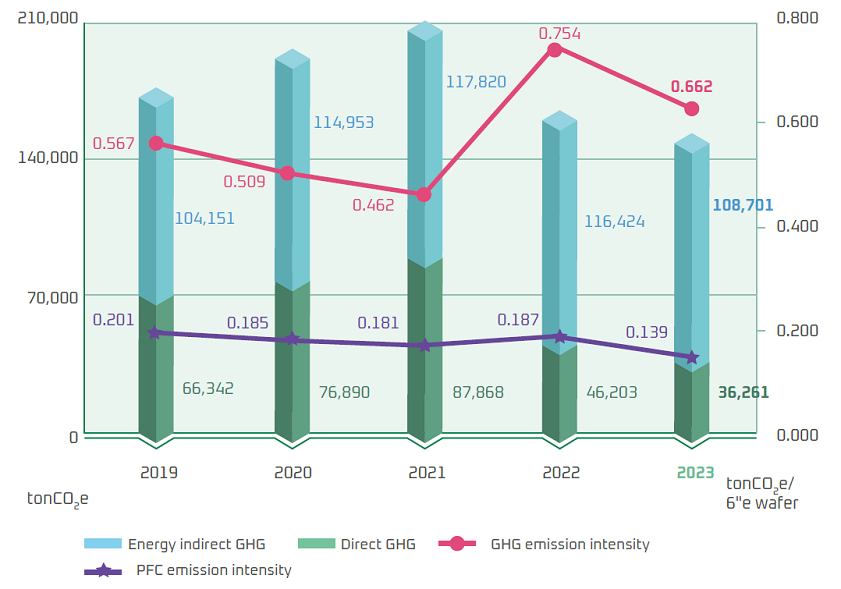
WIN inventoried the direct and energy indirect greenhouse gas emissions in accordance with the Guidelines for Greenhouse Gas Inventories by the Climate Change Administration of Ministry of Environment. In 2024, direct greenhouse gas emissions (Scope 1) was 33,706 metric tons CO2e and the energy indirect greenhouse gas emissions (Scope 2) was 80,096 metric tons CO2e. The GHG emission factor management table announced on the Mandatory Greenhouse Gas Reporting System and the emission factor announced by the Energy Administration, MOEA, were used. Additionally, the GWP data was cited from the IPCC fifth Assessment Report in 2013.
Compared to the 2021 baseline year, greenhouse gas emissions were significantly reduced by 46%, outperforming the SBTi 1.5°C carbon reduction roadmap. The emissions intensity per 6-inch equivalent wafer was 0.37, 0.43, and 0.46 tonCO₂e at the Fab A, Fab B, and Fab C respectively, with an overall average of 0.428 tonCO₂e per wafer, representing a 35% reduction from 2023. WIN 's GHG emissions are mainly from electricity use, followed by PFCs used in processes. Hence, efforts to reduce emissions focused on energy conservation and carbon reduction, as well as the efficiency of local scrubbers.
Direct and Energy Indirect Greenhouse Gas Emissions (Scope 1 and scope 2)
To grasp other indirect greenhouse gas emissions, WIN has conducted Scope 3 inventories since 2020 in accordance with the ISO 14064: 2018 standard. Emission calculations for major categories of indirect GHG emissions are based on the Ministry of Environment’s carbon footprint database and the technical guidelines issued by the World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD). Since 2021, the Company has undergone annual third-party verification in accordance with the ISO 14064-1: 2018 standard.
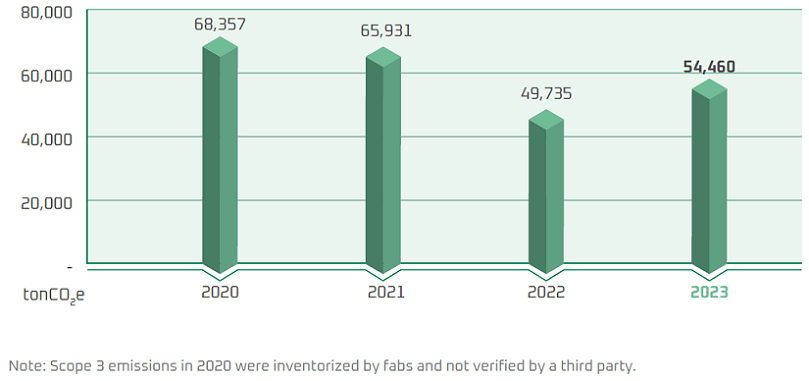
In 2024, the Company’s Scope 3 greenhouse gas emissions totaled 40,635 metric tons CO₂e. This represents a significant 38% reduction compared to the 2021 baseline year, outperforming the SBTi 1.5°C carbon reduction roadmap. The inventory results are shown in the table below, in which products and services purchased upstream had the highest GHG emissions, followed by GHG emissions from purchased fuel and energy. To meet the Scope 3 GHG emissions reduction target, WIN focuses on raw material and electricity reductions and regularly reviews the implementation results.
Other Indirect Greenhouse Gas Emissions (Scope 3)
GHG Reduction Strategy
WIN actively promotes greenhouse gas reduction and uses quantified data from inventories to identify carbon emission hotspots and search for reduction opportunities. The results of the GHG inventory showed that the main source of GHG emissions came from electricity use. Therefore, WIN began implementing the ISO 50001 energy management system in its plants in 2023, and obtained third-party certification. Through energy conservation actions, we improved energy efficiency and switched to energy sources with lower carbon emissions. We switched from the coal-fired steam power used by Fab A to Taipower to reduce indirect GHG emissions from energy.
A secondary source of greenhouse gas emissions is the use of PFCs in production processes, which are gases with high global warming potential. As a result, the Company’s GHG reduction efforts are primarily focused on lowering emissions from fluorinated gases and electricity consumption. Specific management strategies and targets have been established for both areas. Quarterly energy and environmental, health, and safety management review meetings are held to assess implementation progress and future planning, actively driving emission reductions toward the Company’s net-zero goal.
In addition, WIN participates in the greenhouse gas offset project program initiated by the Ministry of Environment. The project was approved and officially registered by the Ministry in 2021. In 2023, the Company replaced local scrubbers in its production lines, significantly reducing PFC greenhouse gas emissions. In line with the project framework, WIN plans to apply for certified GHG reduction credits from the Ministry of Environment in 2025.
Internal Carbon Pricing
In response to the global net-zero carbon emissions and international carbon pricing trends, the Ministry of Environment formulated the Climate Change Response Act in 2023, announcing that carbon fees will be levied in 2025 and the goal of net-zero emissions by 2050. To reduce carbon emission costs, WIN follows the government‘s carbon fee rates as a reference for our carbon reduction planning and management. WIN has adopted a shadow price of TWD 300 per metric ton of CO₂e to support low-carbon decision-making. This internal carbon price applies to Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions, and is used in selected business decisions to evaluate cost-benefit trade-offs and drive energy efficiency. It also supports WIN’s alignment with evolving regulatory frameworks and the achievement of climate-related targets. The mechanism encourages low-carbon investments, integrates climate considerations into risk assessments and strategic planning, and helps identify emission reduction opportunities across the value chain.
In 2024, energy-saving and carbon reduction measures achieved a reduction of 3,793 metric tons CO2e, generating an estimated economic benefit of NT$1,137,900. The Company aims to accelerate the low-carbon transition and innovation to meet our absolute carbon reduction target. Based on greenhouse gas emissions of 110,559 metric tons in 2024, and using the government’s announced carbon fee rate (NT$300 per ton), the estimated annual carbon emission cost amounts to approximately NT$11 million. Furthermore, WIN continues to actively reduce carbon emissions and plans to apply for preferential rates announced by the government (NT$50 or NT$100 per ton) to significantly lower the actual carbon costs.
2024 Emissions Inventory Results
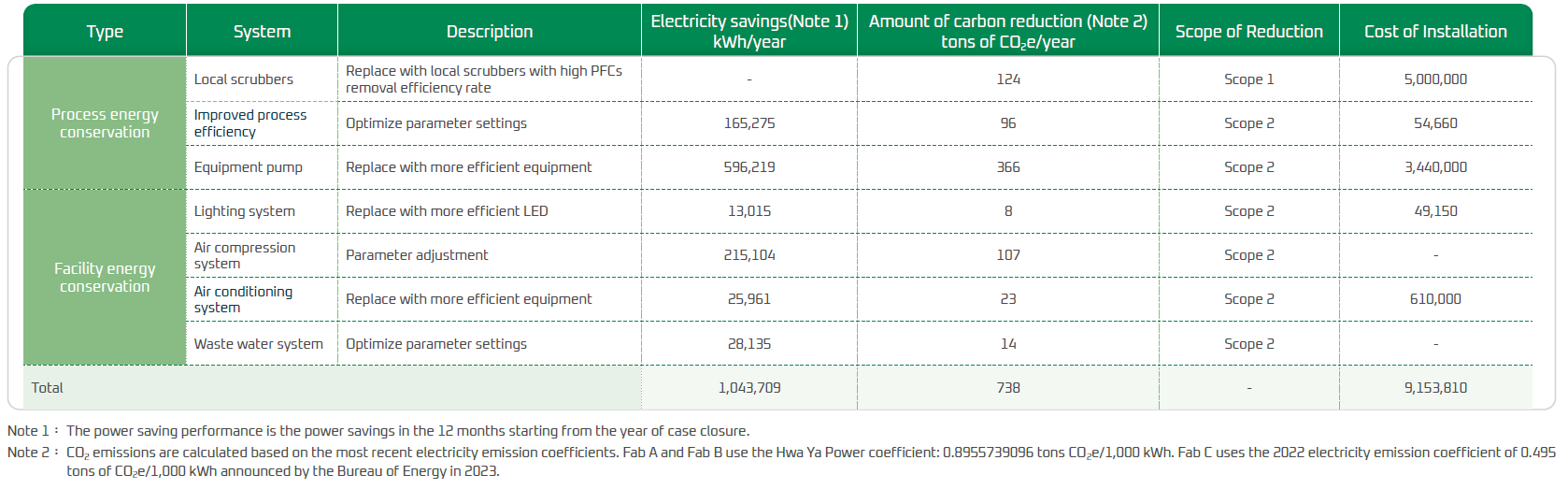
A total of 41 energy conservation plans were completed in 2024, total cost of installation is $41,285,293, which reduced electricity consumption by 1,555,831 kWh and reduced carbon emissions by 3,793 tons CO2e.
Water Resource Management
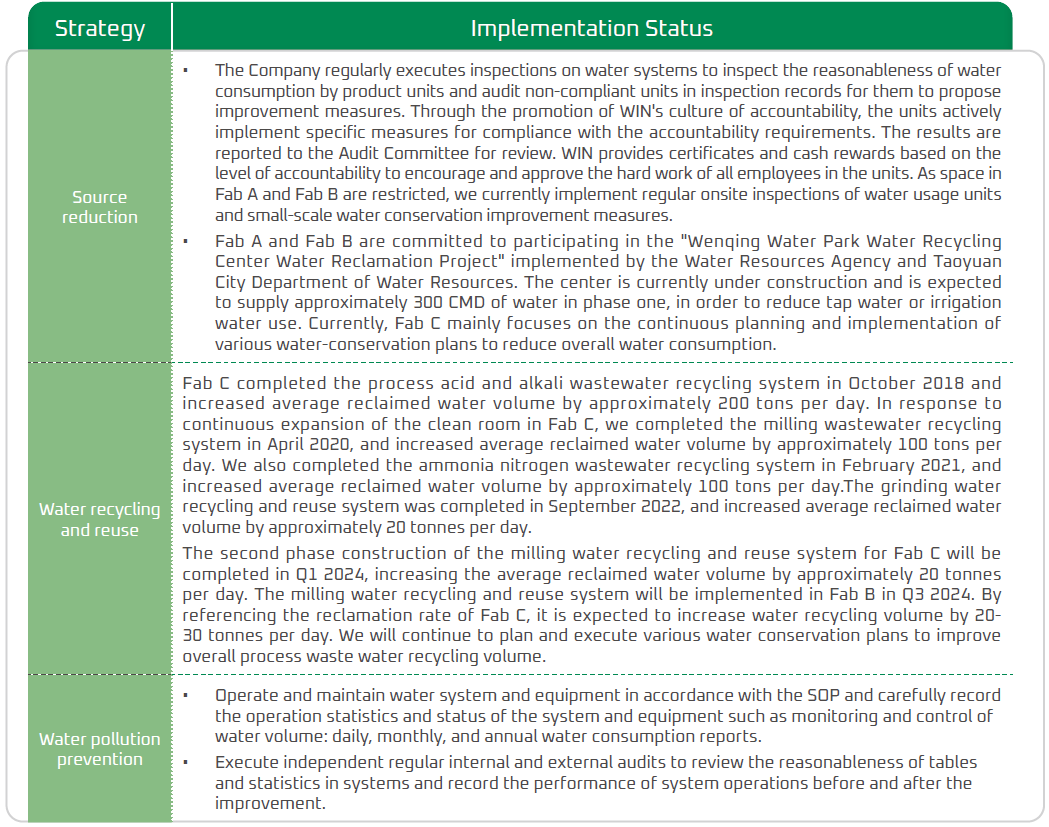
Although the Taoyuan area has been deemed as a low to moderate water stress area, WIN uses the water storage capacity information provided by the Shihmen Reservoir Administration to allocate water supply and optimize operations. In addition to maintaining stable water supply for all plants, we also seek to prevent the impact on production water during droughts. In addition, WIN continues to increase the volume of recycled water used within our facilities and actively participates in the Water Resources Agency's Wenqing Water Park Water Recycling Center Water Reclamation Project. The project was originally scheduled to begin its first phase of water supply in 2025, providing 300 CMD (cubic meters per day) of reclaimed water to WIN. However, due to construction delays by the Taoyuan City Water Department, the supply date has been postponed to 2027. The initial supply volume will be increased to the originally planned second-phase capacity of 500 CMD. In preparation, WIN will complete the construction of its internal reclaimed water system by the end of 2026. Starting with the baseline supply of 300 CMD, the Company will gradually increase its use of reclaimed water following internal testing. This initiative will diversify water sources to ensure a stable supply, reduce reliance on raw water from the Shihmen Reservoir, and lower the risk of water shortages during dry seasons.
WIN obtained ISO 14001 Environmental Management System to reduce our impact on the environment. To fulfill our vision for sustainable water resource circulation and reuse, and in alignment with the CDP Water Security initiative for water intake/discharge efficiency and data transparency, the Company is actively implementing three strategic directions: source reduction, water recycling and reuse, and water pollution prevention. These efforts aim to ensure a stable water supply and continuously improve overall water use efficiency year by year. In addition, WIN is fully aware that the sustainable recycling of water resources involves both improvements by the Company and joint efforts of upstream suppliers. Therefore, we disclosed some information on the water consumption of upstream suppliers and the impact of water security on WIN in the CDP. WIN disclosed information on the Company and upstream suppliers through the CDP "Water Security" rating in 2024 and obtained the highest rating of "A".
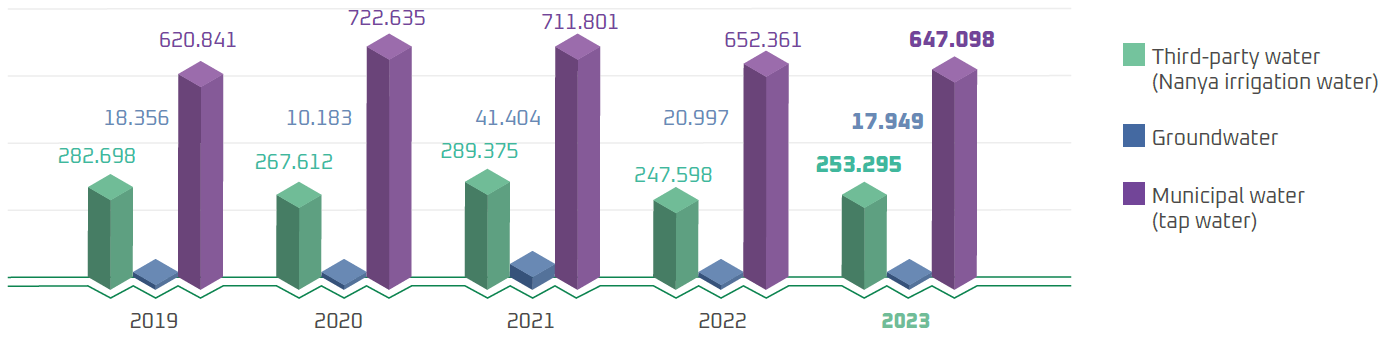
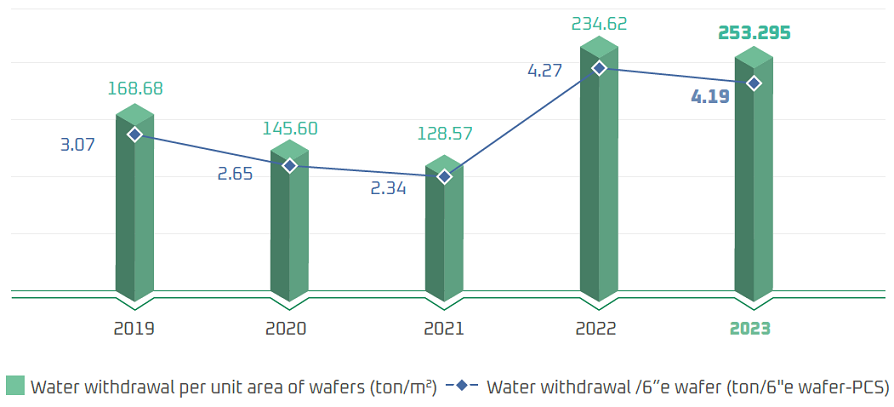
Water Withdrawal
WIN obtains water from tap water, irrigation water (Note), and groundwater. The tap water and irrigation water are sourced from the catchment area of Shihmen Reservoir, which is a freshwater source, and supplied by the water plant (tap water) and Nanya Technology Water Purification Plant. Groundwater is used as emergency backup in the event of drought or water shortage caused by irregular operations of water plants. Due to frequent sediment discharge operations at the Shihmen Reservoir beginning in July 2024, the turbidity of canal water often exceeded 100 NTU, resulting in temporary suspension of supply. As a result, groundwater usage at WIN's Fab A and Fab B remained relatively high throughout 2024.
Note: Irrigation water is defined as water sourced from the Shihmen Dam, which is excess water from farmland irrigation by the Department of Irrigation and Engineering, and processed by the water purification plant of Nanya Technology before it is supplied to WIN for use.
Comparison of Water Withdrawal (Unit: Million liters)
Water Withdrawal per Unit Area of Wafers
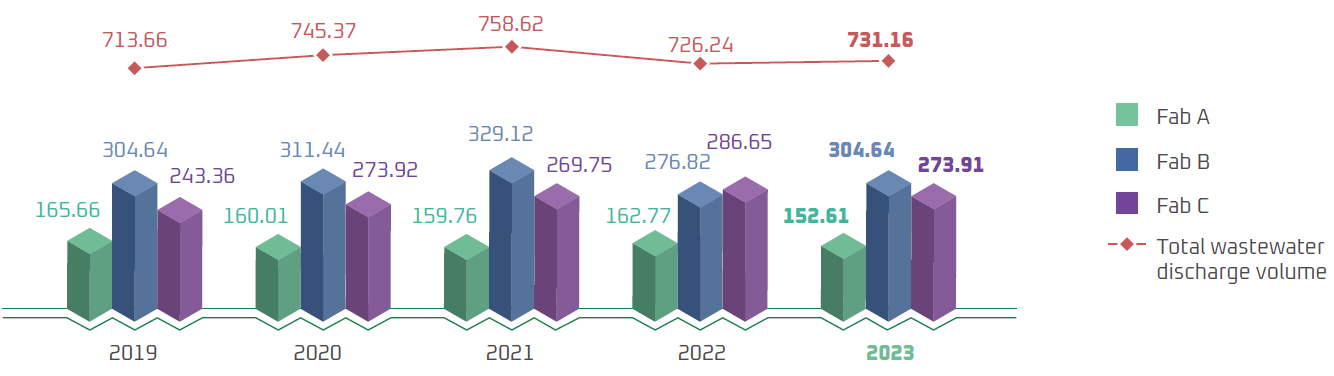
Discharged Water
Fab A and Fab B effluents are collected and processed by Hwaya Technology Park. Fab C effluents are collected and processed by Guishan Industrial Park. To ensure the effectiveness and economic rationale of wastewater treatment, WIN categorizes waste water based on their characteristics and collect individual types of waste water based on such characteristics to reach the effluent standards established by Hwaya Technology Park and Guishan Industrial Park before discharge. We aim to meet the effluent standards established by the Ministry of Environment and avoid causing pollution to downstream water sources.
Total Wastewater Discharge Volume (Unit: Million liters)
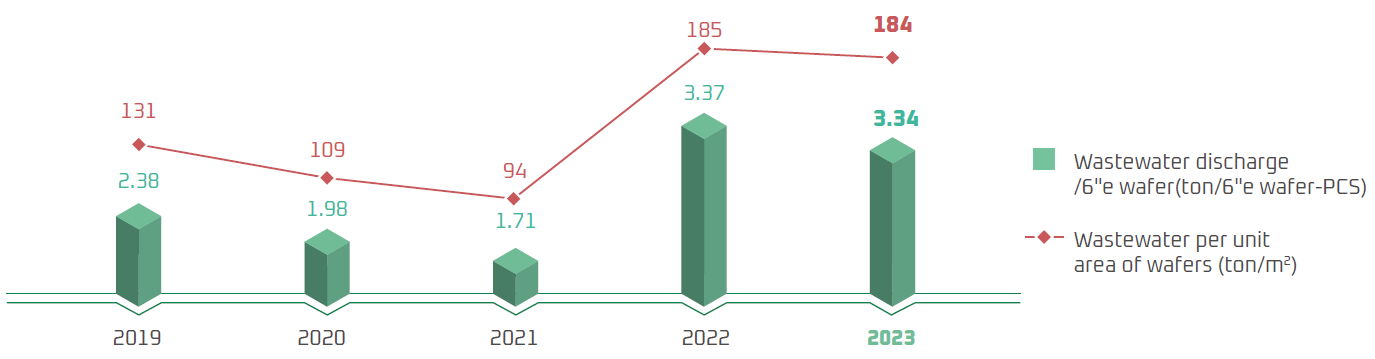
Wastewater Discharge per Wafer
Water Consumption
Water consumption is total water withdrawal minus total water discharge. The main cause of water consumption was evaporation and spray from the cooling water tower. Other causes of water consumption include employee drinking water, environment cleaning water, water in the landscape pool and for watering, cafeteria cooking water, product production, and evaporation from water tanks (water storage system).
Statistics of water consumption (Unit: Million liters)

Water Conservation Plan and Results
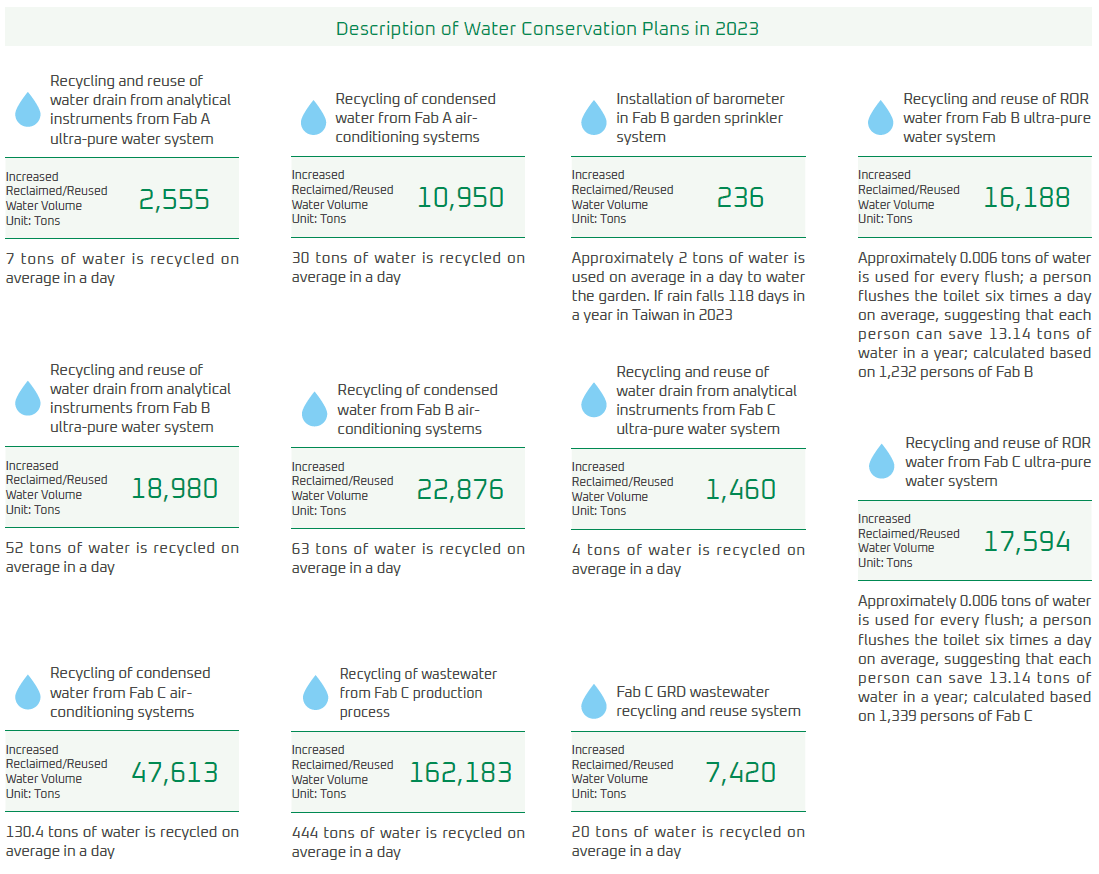
Since 2010, WIN has been consistently implementing various water-saving projects and increasing the overall water recycling rate year by year. In 2024, the volume of recycled water increased to 334,332 cubic meters per year, with a recycling rate of 35%. This represents an increase of 26,277 cubic meters per year in recycled water volume compared to 2023 and a 1.46% increase in the recycling rate from 2023, demonstrating a continued upward trend in the project's recycling rate despite increased water usage due to the LOCAL SCRUBBER.
Waste Management
WIN actively implements source management and waste recycling, encourages every department to propose management plans for reducing process materials to reduce waste or waste liquid, to achieve our annual objective and realize our commitment to zero environmental pollution. For waste produced by the fabs, our first choice of waste vendors is using recycle and reuse, such as precious metals and chemical liquid waste. Precious metals can be recycled to raw materials, thereby improving the value of recycling renewable resources and reducing the impact of waste directed to disposal such as landfilling on the environment.
WIN established an ISO 14001 environmental management system. During the evaluation of environmental considerations, we found that we produce a substantial amount of waste solvents, accounting for 74% of total waste. It is a significant waste-related impact. Waste solvent is mainly produced during the photolithography and etching process of wafer fabrication. To reduce the impact on the environment, WIN sets waste solvent reduction objectives and encourage every department to propose management programs to reduce waste solvent volume. In 2024, general solid waste accounts for about 5% of the total and is mainly general trash generated by business activities. In 2024, all employees participated in occupational safety and environmental protection poster design in a contest to obtain posters for promotion and to strengthen employees’ concept of waste reduction.
WIN has dedicated R&D resources to minimizing waste generation at the source, with a particular focus on reducing process solvent usage. Through ongoing innovation in process optimization and chemical formulation, the company has successfully reduced solvent waste. In 2024, the volume of waste solvent per 6-inch equivalent wafer decreased from 12.70 kg to 10.76 kg, significantly lowering the generation of hazardous waste.
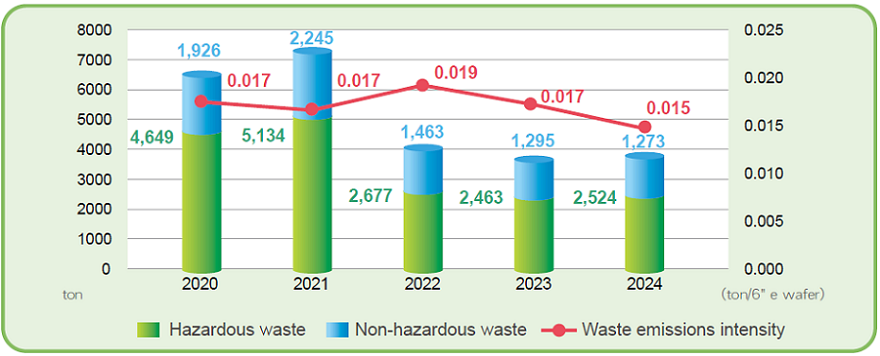
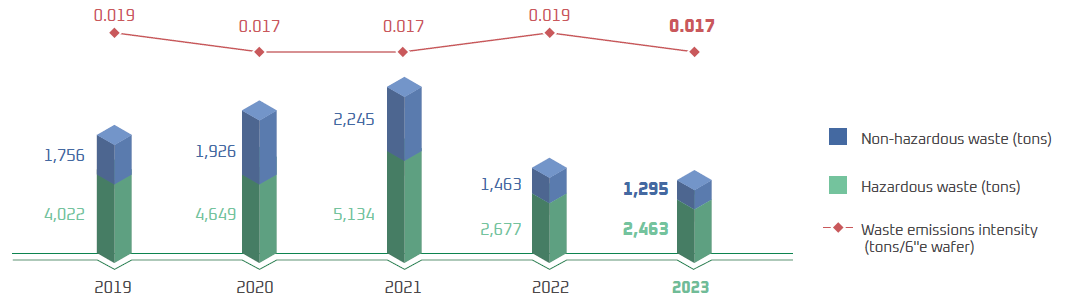
In 2024, WIN produced a total of 3,797 tons of waste, which can be divided into hazardous waste of 2,524 tons and non-hazardous waste of 1,273 tons. Waste disposal methods include diverted from disposal (recycle, reuse, etc.) and directed to disposal (incineration, landfilling, etc.). Of the non-hazardous waste, 344.1 tons is solid waste. 171.2 tons of the solid waste were recycled and reused, 170 tons were disposed of through incineration with energy recovery, 2.3 tons were landfilled, and 0.6 tons were through incineration without energy recovery.
For handling waste, WIN emphasizes recycling and reuse. We commission vendors who give priority to recycle and reuse. 2,958 tons of waste was recycled and the recycling rate is 78% in 2024. If we include the recycling method of incineration with energy recovery, the total amount of waste recycled is 3,324 tons and the recycling rate is 88%.
Waste data
Life Cycle Assessment, Carbon Footprint, Water Footprint
To gain a comprehensive understanding of the environmental impact of our products, WIN conducts Life Cycle Assessments (LCA) of our 6-inch compound semiconductor equivalent wafers across all plants in accordance with the international standards ISO 14040, ISO 14067, and ISO 14046. These assessments cover the entire process from raw material production to wafer manufacturing (cradle-to-gate), analyzing the inputs and outputs at each stage and comparing the potential environmental impacts. In addition to evaluating the 16 environmental impact categories defined by the EU Environmental Footprint (EF), we also assess the product’s life cycle impact on biodiversity, addressing growing global concerns in this area. The Company calculates the carbon and water footprints of our products to better understand potential environmental impacts, allowing us to develop more effective environmental management strategies and continuously improve our environmental performance.
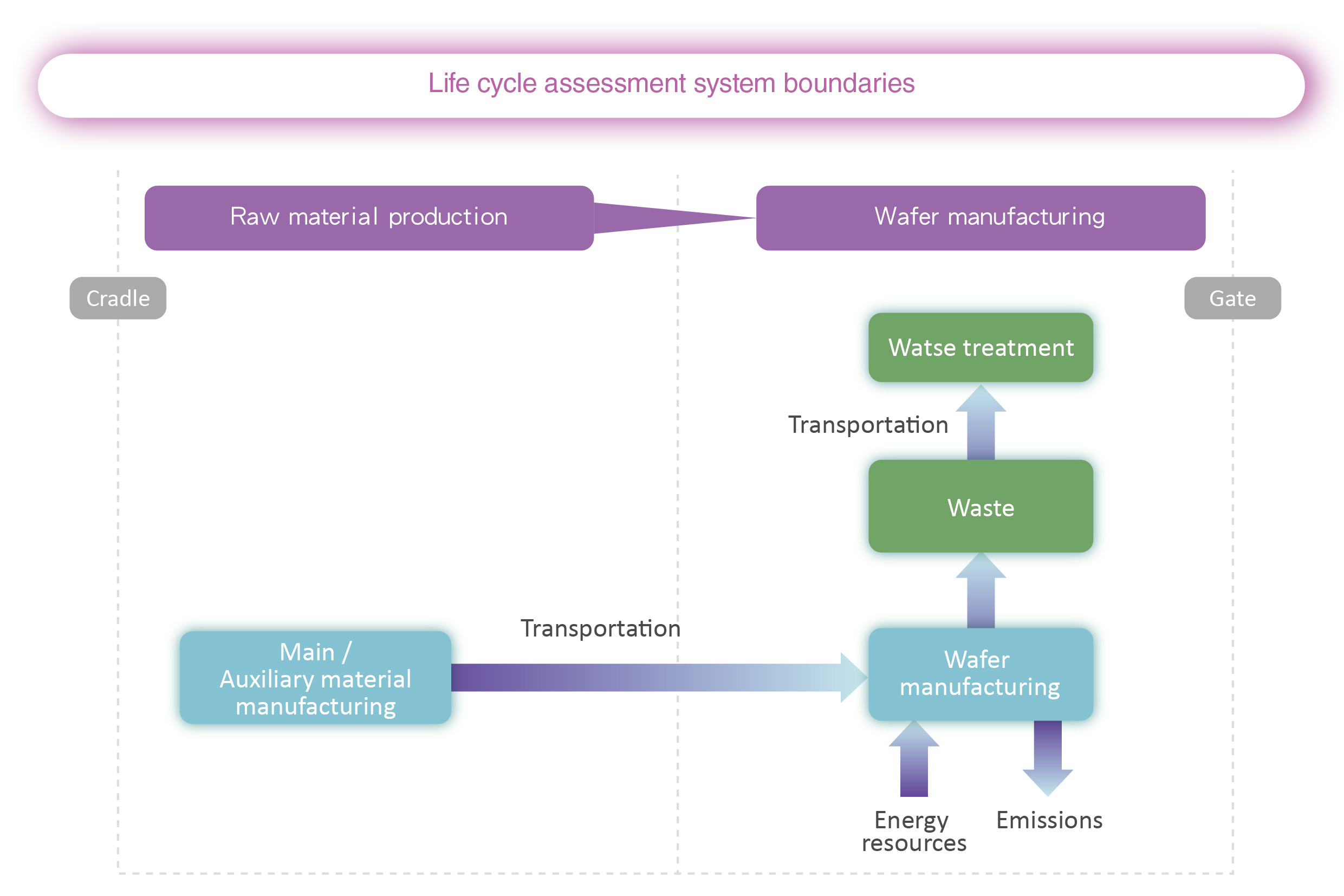
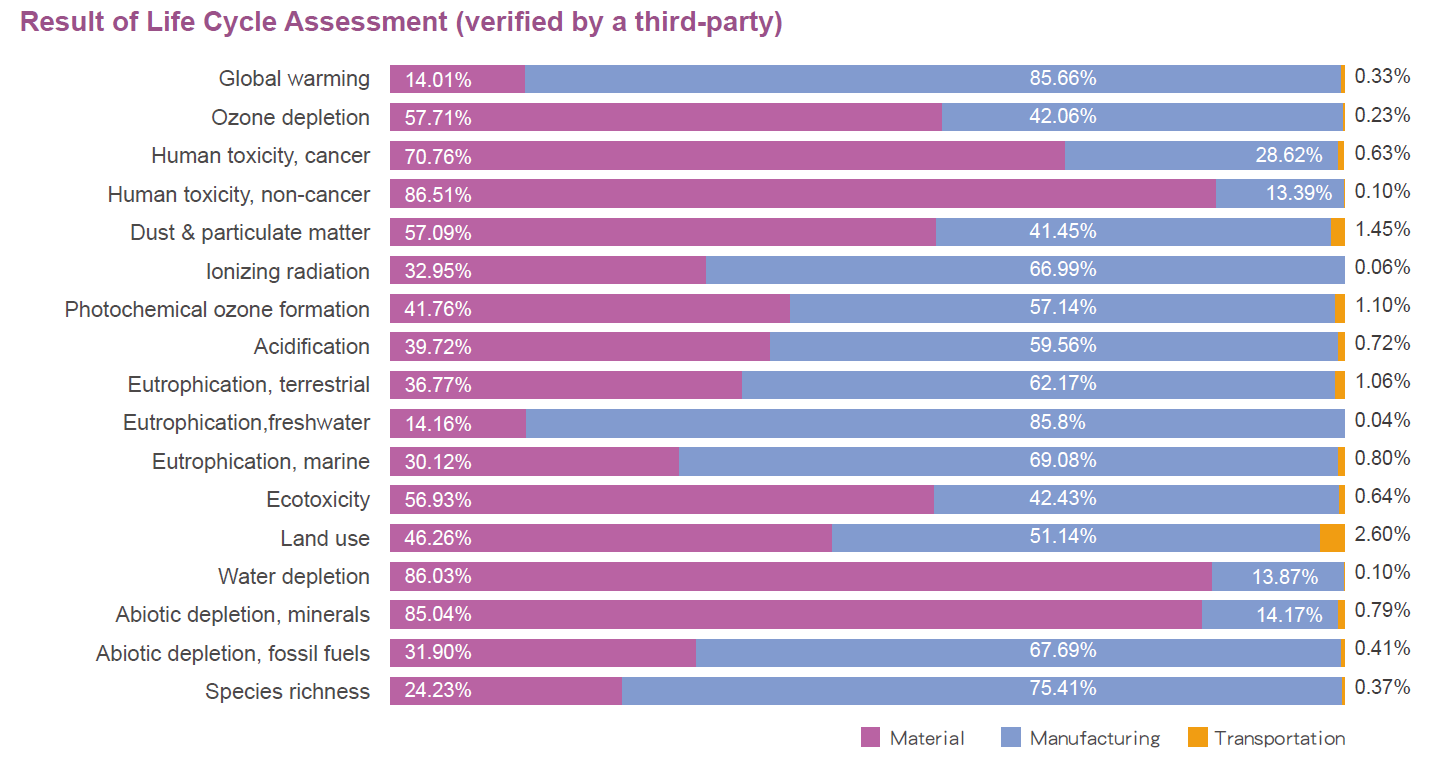
WIN completed the LCAs and carbon and water footprint inventories of Fab A, Fab B, and Fab C in 2023 and 2024, respectively. The results were verified by the third-party company DNV Business Assurance Co., Ltd. to obtain information on the LCA of the Company's 6-inch compound semiconductor equivalent wafers (100% of total production).
Environmental footprint emission hotspots and reduction measures:
- Electricity usage: In 2023, WIN transitioned the power source for Fab A and Fab B facilities from coal-fired generation to lower-carbon electricity provided by Taipower, significantly reducing the environmental footprint associated with electricity consumption. We are also gradually implementing the ISO 50001 Energy Management System across the plants to improve energy efficiency, continuously promote energy-saving measures, and plan for the adoption of renewable energy as part of our ongoing improvement strategy.
- Use of nitrogen gas and organic solvents: In the semiconductor manufacturing process, a variety of gases and chemicals are often required, in which nitrogen gas and organic solvents are the most used. Therefore, they account for a significant proportion of the impact on various environmental footprints and Scope 3 emissions. WIN began reviewing the reduction potential of nitrogen gas in various equipment, machinery, and processes in 2022, leading to gradual adjustments. We set annual reduction targets for nitrogen gas and organic solvents (NMP) in 2024 to reduce Scope 3 GHG emissions and the environmental impact.
For more information, please read full article
DownloadSustainability